5种方法Python将JSON转换为自定义Python对象/类
作者:admin 时间:2021-12-28 9:58:32 浏览:本文将介绍Phyton如何将JSON数据转换为自定义Python对象,即,解析并将JSON转换为Python类。
Python使用json.load() 和 json.loads() 方法从文件或字符串加载 JSON 数据时,它会返回一个dict。如果我们将 JSON 数据直接加载到我们的自定义类型中,我们可以更轻松地操作和使用它。有多种方法可以实现这一点,你可以选择你认为对你的问题更有用的方式。让我们看看如何将 JSON 字符串反序列化为自定义 Python 对象。
Python如何将JSON转换为自定义Python对象
使用namedtuple和object_hook将JSON转换为自定义Python对象
我们可以使用json.loads()和json.load()方法中的object_hook参数,这是一个可选函数,将使用任何对象文字解码的结果(字典dict)调用,所以当我们执行json.loads()时,object_hook的返回值将用字典dict代替。使用此功能,我们可以实现自定义解码器。
正如我们所知json.load()和json.loads()方法将 JSON 转换为dict对象,因此我们需要创建一个自定义函数,我们可以在其中转换dict为自定义 Python 类型。并将这个新创建的函数传递给json.loads方法的object_hook参数。所以我们可以在解码JSON时获得自定义类型。
namedtuple是集合模块下的类。与字典类型对象一样,它包含键并映射到某些值。在这种情况下,我们可以使用键和索引访问元素。
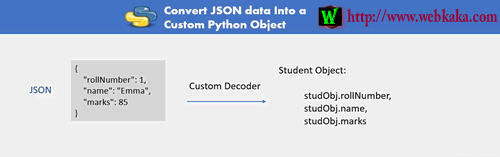
让我们先看一个简单的例子,然后我们才能进入实际的例子。在此示例中,我们将学生JSON数据转换为自定义学生类类型。
import json
from collections import namedtuple
from json import JSONEncoder
def customStudentDecoder(studentDict):
return namedtuple('X', studentDict.keys())(*studentDict.values())
#Assume you received this JSON response
studentJsonData = '{"rollNumber": 1, "name": "Emma"}'
# Parse JSON into an object with attributes corresponding to dict keys.
student = json.loads(studentJsonData, object_hook=customStudentDecoder)
print("After Converting JSON Data into Custom Python Object")
print(student.rollNumber, student.name)
输出:
After Converting JSON Data into Custom Python Object
1 Emma
如你所见,我们将 JSON 字符串格式的 JSON 数据转换为自定义 Python 对象 Student。现在,我们可以使用 dot(.) 运算符访问其成员。
现在,让我们看看使用复杂 Python 对象的实时场景。我们需要将自定义 Python 对象转换为 JSON。此外,我们想从 JSON 构造一个自定义的 Python 对象。
在这个例子中,我们使用了两个类Student和Marks。Marks类是Student类的成员。
- 首先,我们将 Student 类编码为 JSON 数据。
- 然后,我们使用相同的 JSON 数据将其解码为 Student 类。
现在让我们看看例子。
import json
from collections import namedtuple
from json import JSONEncoder
class Student:
def __init__(self, rollNumber, name, marks):
self.rollNumber, self.name, self.marks = rollNumber, name, marks
class Marks:
def __init__(self, english, geometry):
self.english, self.geometry = english, geometry
class StudentEncoder(JSONEncoder):
def default(self, o):
return o.__dict__
def customStudentDecoder(studentDict):
return namedtuple('X', studentDict.keys())(*studentDict.values())
marks = Marks(82, 74)
student = Student(1, "Emma", marks)
# dumps() produces JSON in native str format. if you want to writ it in file use dump()
studentJson = json.dumps(student, indent=4, cls=StudentEncoder)
print("Student JSON")
print(studentJson)
# Parse JSON into an object with attributes corresponding to dict keys.
studObj = json.loads(studentJson, object_hook=customStudentDecoder)
print("After Converting JSON Data into Custom Python Object")
print(studObj.rollNumber, studObj.name, studObj.marks.english, studObj.marks.geometry)
输出:
Student JSON
{
"rollNumber": 1,
"name": "Emma",
"marks": {
"english": 82,
"geometry": 74
}
}
After Converting JSON Data into Custom Python Object
1 Emma 82 74
使用 types.SimpleNamespace 和 object_hook 将 JSON 转换为自定义 Python 对象
我们可以用types.SimpleNamespace作为 JSON 对象的容器。与命名元组解决方案相比,它具有以下优势:
- 它的执行时间更少,因为它没有为每个对象创建一个类。
- 它精确而简单。
在本例中,我们将使用types.SimpleNamespace和object_hook将 JSON 数据转换为自定义 Python 对象。
from __future__ import print_function
import json
from json import JSONEncoder
try:
from types import SimpleNamespace as Namespace
except ImportError:
# Python 2.x fallback
from argparse import Namespace
class Student:
def __init__(self, rollNumber, name, marks):
self.rollNumber, self.name, self.marks = rollNumber, name, marks
class Marks:
def __init__(self, english, geometry):
self.english, self.geometry = english, geometry
class StudentEncoder(JSONEncoder):
def default(self, o): return o.__dict__
marks = Marks(82, 74)
student = Student(1, "Emma", marks)
# dumps() produces JSON in native str format. if you want to writ it in file use dump()
studentJsonData = json.dumps(student, indent=4, cls=StudentEncoder)
print("Student JSON")
print(studentJsonData)
# Parse JSON into an custom Student object.
studObj = json.loads(studentJsonData, object_hook=lambda d: Namespace(**d))
print("After Converting JSON Data into Custom Python Object using SimpleNamespace")
print(studObj.rollNumber, studObj.name, studObj.marks.english, studObj.marks.geometry)
输出:
Student JSON
{
"rollNumber": 1,
"name": "Emma",
"marks": {
"english": 82,
"geometry": 74
}
}
After Converting JSON Data into Custom Python Object using SimpleNamespace
1 Emma 82 74
使用 JSONDecoder 类的对象解码将 JSON 数据转换为自定义 Python 对象
我们可以使用 json模块的json.JSONDecoder类来专门进行 JSON 对象解码,这里我们可以将 JSON 对象解码为自定义的 Python 类型。
我们需要在一个类中创建一个新函数,该函数将负责检查 JSON 字符串中的对象类型,在获取 JSON 数据中的正确类型后,我们可以构建我们的对象。
让我们看看例子。
import json
class Student(object):
def __init__(self, rollNumber, name, marks):
self.rollNumber = rollNumber
self.name = name
self.marks = marks
def studentDecoder(obj):
if '__type__' in obj and obj['__type__'] == 'Student':
return Student(obj['rollNumber'], obj['name'], obj['marks'])
return obj
studentObj = json.loads('{"__type__": "Student", "rollNumber":1, "name": "Ault kelly", "marks": 78}',
object_hook=studentDecoder)
print("Type of decoded object from JSON Data")
print(type(studentObj))
print("Student Details")
print(studentObj.rollNumber, studentObj.name, studentObj.marks)
输出:
Type of decoded object from JSON Data
<class '__main__.Student'>
Student Details
1 Ault kelly 78
使用 jsonpickle 模块将 JSON 数据转换为自定义 Python 对象
jsonpickle 是一个 Python 库,旨在处理复杂的 Python 对象。你可以使用 jsonpickle 对复杂的 Python 和 JSON 数据进行序列化和反序列化。
Python 内置的 JSON 模块只能处理 Python 原语。对于任何自定义 Python 对象,我们都需要编写自己的 JSONEncoder 和 Decoder。
使用 jsonpickle 我们将执行以下操作:
- 首先,我们将使用 jsonpickle 将 Student 对象编码为 JSON
- 然后我们将Student JSON解码成Student对象
现在,让我们看看将 JSON 数据转换为自定义 Python 对象的 jsonpickle 示例。
import json
import jsonpickle
from json import JSONEncoder
class Student(object):
def __init__(self, rollNumber, name, marks):
self.rollNumber = rollNumber
self.name = name
self.marks = marks
class Marks(object):
def __init__(self, english, geometry):
self.english = english
self.geometry = geometry
marks = Marks(82, 74)
student = Student(1, "Emma", marks)
print("Encode Object into JSON formatted Data using jsonpickle")
studentJSON = jsonpickle.encode(student)
print(studentJSON)
print("Decode and Convert JSON into Object using jsonpickle")
studentObject = jsonpickle.decode(studentJSON)
print("Object type is: ", type(studentObject))
print("Student Details")
print(studentObject.rollNumber, studentObject.name, studentObject.marks.english, studentObject.marks.geometry)
输出:
Encode Object into JSON formatted Data using jsonpickle
{"marks": {"english": 82, "geometry": 74, "py/object": "__main__.Marks"}, "name": "Emma", "py/object": "__main__.Student", "rollNumber": 1}
Decode JSON formatted Data using jsonpickle
1 Emma 82 74
新建一个对象,将结果字典作为map传递,将JSON数据转换为自定义的Python对象
正如我们所知json.loads()和json.load()方法返回一个dict对象。我们可以通过将dict对象作为参数传递给 Student 对象构造函数来构造一个新的自定义对象。即,我们可以将dict对象映射到自定义对象。
import json
from json import JSONEncoder
class Student(object):
def __init__(self, rollNumber, name, *args, **kwargs):
self.rollNumber = rollNumber
self.name = name
class StudentEncoder(JSONEncoder):
def default(self, o):
return o.__dict__
student = Student(1, "Emma")
# encode Object it
studentJson = json.dumps(student, cls=StudentEncoder, indent=4)
#Deconde JSON
resultDict = json.loads(studentJson)
print("Converting JSON into Python Object")
studentObj = Student(**resultDict)
print("Object type is: ", type(studentObj))
print("Student Details")
print(studentObj.rollNumber, studentObj.name)
输出:
Converting JSON into Python Object
Object type is: <class '__main__.Student'>
Student Details
1 Emma
总结
本文通过几种方法,介绍了Python如何将JSON转换为自定义Python对象/Python类。